JAJSGG2C October 2018 – June 2019 ADS125H02
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3 Feature Description
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10.5 Programming
- 10.6
Register Map
- 10.6.1 Device Identification (ID) Register (address = 00h) [reset = 6xh]
- 10.6.2 Main Status (STATUS0) Register (address = 01h) [reset = 01h]
- 10.6.3 Mode 0 (MODE0) Register (address = 02h) [reset = 24h]
- 10.6.4 Mode 1 (MODE1) Register (address = 03h) [reset = 01h]
- 10.6.5 Mode 2 (MODE2) Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 10.6.6 Mode 3 (MODE3) Register (address = 05h) [reset = 00h]
- 10.6.7 Reference Configuration (REF) Register (address = 06h) [reset = 05h]
- 10.6.8 Offset Calibration (OFCALx) Registers (address = 07h, 08h, 09h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 10.6.9 Full-Scale Calibration (FSCALx) Registers (address = 0Ah, 0Bh, 0Ch) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 10.6.10 Current Source Multiplexer (I_MUX) Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = FFh]
- 10.6.11 Current Source Magnitude (I_MAG) Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 10.6.12 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 10.6.13 MODE4 (MODE4) Register (address = 10h) [reset = 50h]
- 10.6.14 PGA Alarm (STATUS1) Register (address = 11h) [reset = xxh]
- 10.6.15 Status 2 (STATUS2) Register (address = 12h) [reset = 0xh]
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 15メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RHB|32
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RHB|32
発注情報
10.3.8.2 FIR Filter
The finite impulse response (FIR) filter is a coefficient-based filter that provides an overall low-pass filter response. The filter provides simultaneous rejection of 50-Hz and 60-Hz line cycle frequencies and related harmonics at data rates of 2.5 SPS, 5 SPS, 10 SPS, and 20 SPS. The conversion latency of the FIR filter is a single cycle. (See Table 8 for latency of all filter settings). As illustrated in Figure 65, the FIR filter section receives data from the second-stage sinc filter. The FIR filter section decimates the data to yield the output data rate of 20 SPS. A first-order variable-decimation averaging filter (sinc1) yields 10 SPS, 5 SPS, and 2.5 SPS.
As shown in Figure 74 and Figure 75, the FIR filter frequency response has a series of response nulls that are positioned close to 50 Hz and 60 Hz. The response nulls repeat near the harmonics of 50 Hz and 60 Hz.
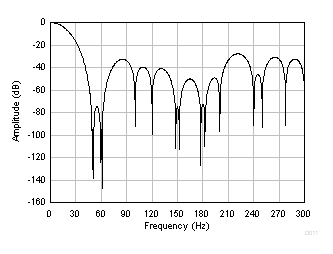 Figure 74. FIR Frequency Response (20 SPS)
Figure 74. FIR Frequency Response (20 SPS) 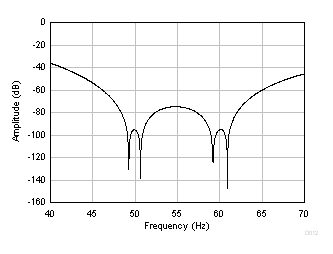 Figure 75. FIR Frequency Response Detail (20 SPS)
Figure 75. FIR Frequency Response Detail (20 SPS) Figure 76 shows the FIR filter response at 10 SPS. New frequency nulls are superimposed to the nulls in Figure 74 as a result of the variable averager. The first of the combined response nulls occurs at 10 Hz. Additional nulls occur at folded frequencies around multiples of 20 Hz. The first of the 10 SPS folded null frequencies is shown in Figure 76 at 10 Hz, 30 Hz, 70 Hz, 90 Hz, and so on.
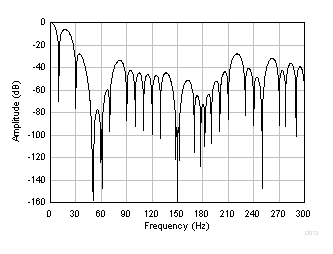 Figure 76. FIR Frequency Response (10 SPS)
Figure 76. FIR Frequency Response (10 SPS) Similar to the response of the sinc filter, the overall FIR filter frequency has a low-pass response that rolls off high frequencies. The response is such that the FIR filter limits the bandwidth of the input signal. The signal bandwidth depends on the output data rate. Table 6 lists the –3-dB filter bandwidth of the FIR filter. The total system bandwidth is the combined response of the digital filter, the PGA antialias filter, and external filters.
Table 6. FIR Filter Bandwidth
| DATA RATE (SPS) | –3-dB BANDWIDTH (Hz) |
|---|---|
| 2.5 | 1.2 |
| 5 | 2.4 |
| 10 | 4.7 |
| 20 | 13 |