SNAS404B May 2007 – January 2016 LMX2487E
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 R0 Register
- 8.6.2 R1 REGISTER
- 8.6.3 R2 Register
- 8.6.4 R3 Register
- 8.6.5
R4 Register
- 8.6.5.1 MUX[3:0] Frequency Out and Lock Detect MUX
- 8.6.5.2 IF_P - IF Prescaler
- 8.6.5.3 RF_CPP - RF PLL Charge Pump Polarity
- 8.6.5.4 IF_CPP - IF PLL Charge Pump Polarity
- 8.6.5.5 OSC_OUT Oscillator Output Buffer Enable
- 8.6.5.6 OSC2X - Oscillator Doubler Enable
- 8.6.5.7 FM[1:0] - Fractional Mode
- 8.6.5.8 DITH[1:0] - Dithering Control
- 8.6.5.9 ATPU - PLL Automatic Power Up
- 8.6.6 R5 Register
- 8.6.7 R6 Register
- 8.6.8 R7 Register
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RTW|24
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTW|24
発注情報
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
This device ideal for use in a broad class of applications, especially those requiring low current consumption and low fractional spurs. For applications that only need a single PLL, the unused PLL can be powered down and will not draw any extra current or generate any spurs or crosstalk.
9.2 Typical Application
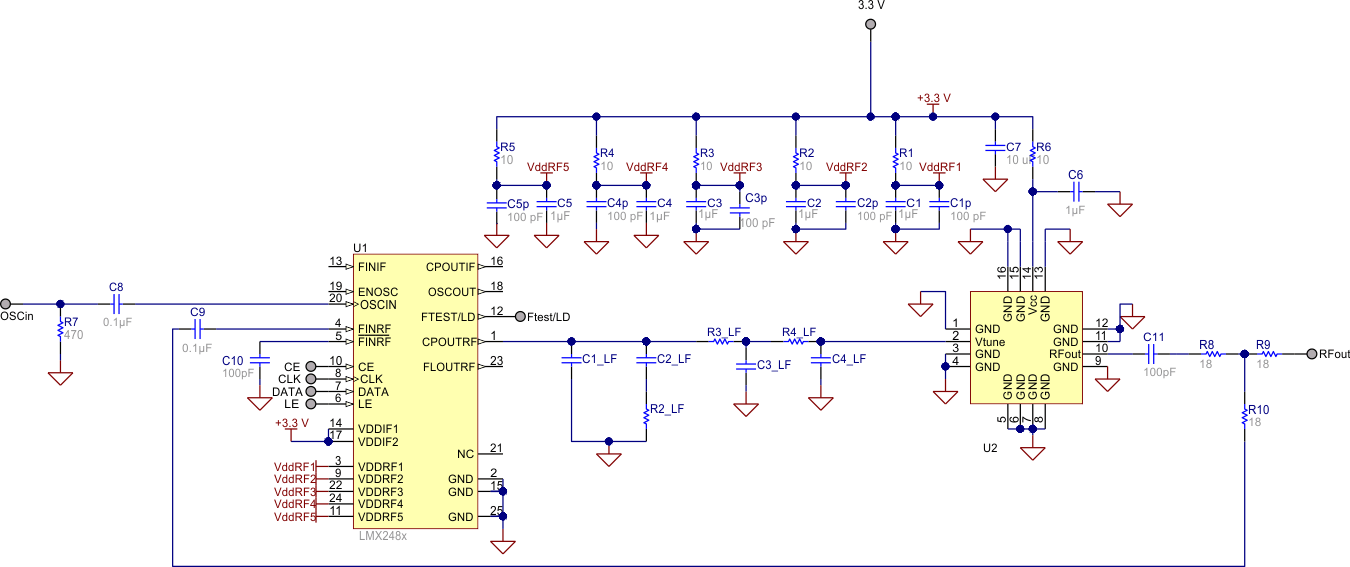 Figure 25. Typical Application
Figure 25. Typical Application
9.2.1 Design Requirements
Table 47 lists the design parameters of the LMX2487E.
Table 47. Design Requirements
| PARAMETER | VALUE | |
|---|---|---|
| PM | Phase Margin | 48.6 degrees |
| BW | Loop Bandwidth | 9.3 KHz |
| T3/T1 | Pole Ratio | 39.70% |
| T4/T3 | 39.20% | |
| KPD | Charge Pump Gain | 8X (760 µA) |
| fPD | Phase Detector Frequency | 20 MHz |
| fVCO | VCO Frequency | 6000-6030 |
| Vcc | Supply Votlage | 3 V |
| KVCO | VCO Gain | 20 MHz/V |
| CVCO | VCO Input Capacitance | 50 pF |
| C1_LF | Loop Filter Component | 2.2 nF |
| C2_LF | 39 nF | |
| C3_LF | 220 pF | |
| C4_LF | 100 pF | |
| R2_LF | 1.2 kΩ | |
| R3_LF | 4.7 kΩ | |
| R4_LF | 10 kΩ | |
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The design of the loop filter involves balancing requirements of lock time, spurs, and phase noise. This design is fairly involved, but the TI website has references, design tools, and simulation tools cover the loop filter design and simulation in depth.
9.2.3 Application Curves
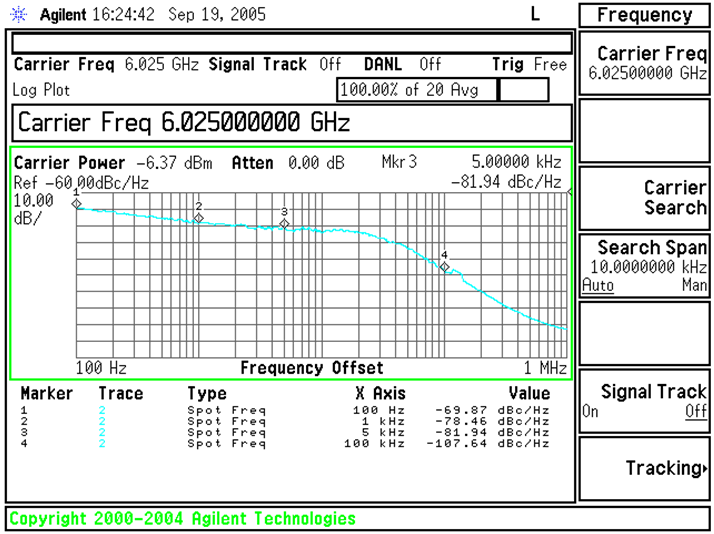 Figure 26. Phase Noise
Figure 26. Phase Noise
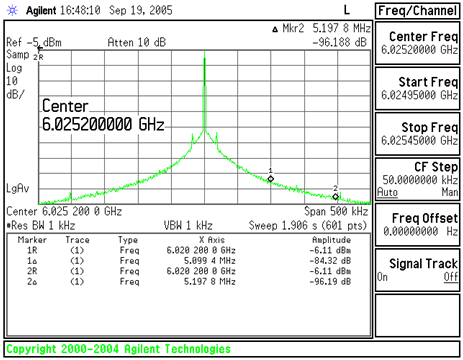 Figure 27. Fractional Spurs at 200-kHz Offset
Figure 27. Fractional Spurs at 200-kHz Offset