JAJSDR1 September 2017 REF2125
PRODUCTION DATA.
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Figure 31 illustrates an example of a PCB layout for a data acquisition system using the REF2125. Some key considerations are:
- Connect low-ESR, 0.1-μF ceramic bypass capacitors at VIN, VREF of the REF2125.
- Decouple other active devices in the system per the device specifications.
- Using a solid ground plane helps distribute heat and reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) noise pickup.
- Place the external components as close to the device as possible. This configuration prevents parasitic errors (such as the Seebeck effect) from occurring.
- Do not run sensitive analog traces in parallel with digital traces. Avoid crossing digital and analog traces if possible, and only make perpendicular crossings when absolutely necessary.
11.2 Layout Example
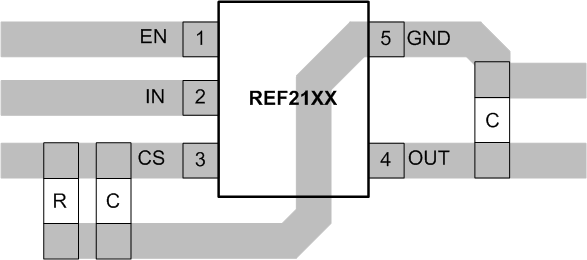 Figure 31. Layout Example
Figure 31. Layout Example