JAJSHM4U April 2001 – July 2019 TMS320F2810 , TMS320F2811 , TMS320F2812
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1デバイスの概要
- 2改訂履歴
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 5.3 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for 179-Ball ZHH Package
- 5.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for 179-Ball GHH Package
- 5.9 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for 176-Pin PGF Package
- 5.10 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for 128-Pin PBK Package
- 5.11 Thermal Design Considerations
- 5.12
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.12.1 Timing Parameter Symbology
- 5.12.2 Power Supply Sequencing
- 5.12.3 Reset Timing
- 5.12.4 Clock Specifications
- 5.12.5
Peripherals
- 5.12.5.1 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) – Output Timing
- 5.12.5.2 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) – Input Timing
- 5.12.5.3 Event Manager Interface
- 5.12.5.4 Low-Power Mode Wakeup Timing
- 5.12.5.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Master Mode Timing
- 5.12.5.6 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Slave Mode Timing
- 5.12.5.7 External Interface (XINTF) Timing
- 5.12.5.8 XINTF Signal Alignment to XCLKOUT
- 5.12.5.9 External Interface Read Timing
- 5.12.5.10 External Interface Write Timing
- 5.12.5.11
External Interface Ready-on-Read Timing With One External Wait State
- Table 5-31 External Memory Interface Read Switching Characteristics (Ready-on-Read, 1 Wait State)
- Table 5-32 External Memory Interface Read Timing Requirements (Ready-on-Read, 1 Wait State)
- Table 5-33 Synchronous XREADY Timing Requirements (Ready-on-Read, 1 Wait State)
- Table 5-34 Asynchronous XREADY Timing Requirements (Ready-on-Read, 1 Wait State)
- 5.12.5.12 External Interface Ready-on-Write Timing With One External Wait State
- 5.12.5.13 XHOLD and XHOLDA
- 5.12.5.14 XHOLD/XHOLDA Timing
- 5.12.5.15
On-Chip Analog-to-Digital Converter
- Table 5-40 ADC Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted)
- Table 5-41 ADC Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted)—AC Specifications
- Table 5-42 ADC Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted)—DC Specifications
- 5.12.5.15.1 Current Consumption for Different ADC Configurations
- 5.12.5.15.2 ADC Power-Up Control Bit Timing
- 5.12.5.15.3 Detailed Description
- 5.12.5.15.4 Sequential Sampling Mode (Single-Channel) (SMODE = 0)
- 5.12.5.15.5 Simultaneous Sampling Mode (Dual-Channel) (SMODE = 1)
- 5.12.5.15.6 Definitions of Specifications and Terminology
- 5.12.5.16
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) Timing
- 5.12.5.16.1 McBSP Transmit and Receive Timing
- 5.12.5.16.2
McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing
- Table 5-49 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 5-50 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 5-51 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 5-52 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 5-53 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 5-54 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 5-55 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 5-56 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- 5.12.6 Emulator Connection Without Signal Buffering for the DSP
- 5.12.7 Interrupt Timing
- 5.12.8 Flash Timing
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1
Brief Descriptions
- 6.1.1 C28x CPU
- 6.1.2 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 6.1.3 Peripheral Bus
- 6.1.4 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 6.1.5 External Interface (XINTF) (F2812 Only)
- 6.1.6 Flash
- 6.1.7 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 6.1.8 L0, L1, H0 SARAMs
- 6.1.9 Boot ROM
- 6.1.10 Security
- 6.1.11 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 6.1.12 External Interrupts (XINT1, XINT2, XINT13, XNMI)
- 6.1.13 Oscillator and PLL
- 6.1.14 Watchdog
- 6.1.15 Peripheral Clocking
- 6.1.16 Low-Power Modes
- 6.1.17 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2 (PFn)
- 6.1.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 6.1.19 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 6.1.20 Control Peripherals
- 6.1.21 Serial Port Peripherals
- 6.2
Peripherals
- 6.2.1 32-Bit CPU-Timers 0/1/2
- 6.2.2
Event Manager Modules (EVA, EVB)
- 6.2.2.1 General-Purpose (GP) Timers
- 6.2.2.2 Full-Compare Units
- 6.2.2.3 Programmable Deadband Generator
- 6.2.2.4 PWM Waveform Generation
- 6.2.2.5 Double Update PWM Mode
- 6.2.2.6 PWM Characteristics
- 6.2.2.7 Capture Unit
- 6.2.2.8 Quadrature-Encoder Pulse (QEP) Circuit
- 6.2.2.9 External ADC Start-of-Conversion
- 6.2.3 Enhanced Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Module
- 6.2.4 Enhanced Controller Area Network (eCAN) Module
- 6.2.5 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) Module
- 6.2.6 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Module
- 6.2.7 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module
- 6.2.8 GPIO MUX
- 6.3 Memory Maps
- 6.4 Register Map
- 6.5 Device Emulation Registers
- 6.6 External Interface, XINTF (F2812 Only)
- 6.7 Interrupts
- 6.8 System Control
- 6.9 OSC and PLL Block
- 6.10 PLL-Based Clock Module
- 6.11 External Reference Oscillator Clock Option
- 6.12 Watchdog Block
- 6.13 Low-Power Modes Block
- 6.1
Brief Descriptions
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 9メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PBK|128
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PBK|128
発注情報
6.2.8 GPIO MUX
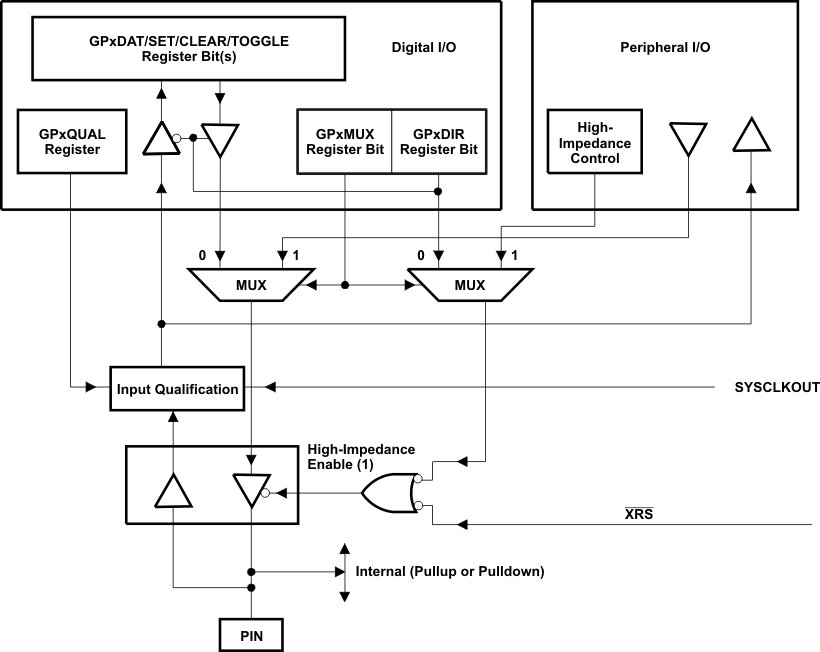
The GPIO Mux registers are used to select the operation of shared pins on the F281x devices. The pins can be individually selected to operate as “Digital I/O” or connected to “Peripheral I/O” signals (via the GPxMUX registers). If selected for “Digital I/O”mode, registers are provided to configure the pin direction (via the GPxDIR registers) and to qualify the input signal to remove unwanted noise (via the GPxQUAL) registers). Table 6-13 lists the GPIO Mux Registers.
Table 6-13 GPIO Mux Registers(1)(2)(3)
| NAME | ADDRESS | SIZE (x16) | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPAMUX | 0x00 70C0 | 1 | GPIO A Mux Control Register |
| GPADIR | 0x00 70C1 | 1 | GPIO A Direction Control Register |
| GPAQUAL | 0x00 70C2 | 1 | GPIO A Input Qualification Control Register |
| Reserved | 0x00 70C3 | 1 | |
| GPBMUX | 0x00 70C4 | 1 | GPIO B Mux Control Register |
| GPBDIR | 0x00 70C5 | 1 | GPIO B Direction Control Register |
| GPBQUAL | 0x00 70C6 | 1 | GPIO B Input Qualification Control Register |
| Reserved | 0x00 70C7 | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70C8 | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70C9 | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70CA | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70CB | 1 | |
| GPDMUX | 0x00 70CC | 1 | GPIO D Mux Control Register |
| GPDDIR | 0x00 70CD | 1 | GPIO D Direction Control Register |
| GPDQUAL | 0x00 70CE | 1 | GPIO D Input Qualification Control Register |
| Reserved | 0x00 70CF | 1 | |
| GPEMUX | 0x00 70D0 | 1 | GPIO E Mux Control Register |
| GPEDIR | 0x00 70D1 | 1 | GPIO E Direction Control Register |
| GPEQUAL | 0x00 70D2 | 1 | GPIO E Input Qualification Control Register |
| Reserved | 0x00 70D3 | 1 | |
| GPFMUX | 0x00 70D4 | 1 | GPIO F Mux Control Register |
| GPFDIR | 0x00 70D5 | 1 | GPIO F Direction Control Register |
| Reserved | 0x00 70D6 | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70D7 | 1 | |
| GPGMUX | 0x00 70D8 | 1 | GPIO G Mux Control Register |
| GPGDIR | 0x00 70D9 | 1 | GPIO G Direction Control Register |
| Reserved | 0x00 70DA | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70DB | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70DC – 0x00 70DF | 4 |
If configured for ”Digital I/O” mode, additional registers are provided for setting individual I/O signals (via the GPxSET registers), for clearing individual I/O signals (via the GPxCLEAR registers), for toggling individual I/O signals (via the GPxTOGGLE registers), or for reading/writing to the individual I/O signals (via the GPxDAT registers). Table 6-14 lists the GPIO Data Registers. For more information, see the TMS320x281x DSP System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide.
Table 6-14 GPIO Data Registers(1)(2)
| NAME | ADDRESS | SIZE (x16) | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPADAT | 0x00 70E0 | 1 | GPIO A Data Register |
| GPASET | 0x00 70E1 | 1 | GPIO A Set Register |
| GPACLEAR | 0x00 70E2 | 1 | GPIO A Clear Register |
| GPATOGGLE | 0x00 70E3 | 1 | GPIO A Toggle Register |
| GPBDAT | 0x00 70E4 | 1 | GPIO B Data Register |
| GPBSET | 0x00 70E5 | 1 | GPIO B Set Register |
| GPBCLEAR | 0x00 70E6 | 1 | GPIO B Clear Register |
| GPBTOGGLE | 0x00 70E7 | 1 | GPIO B Toggle Register |
| Reserved | 0x00 70E8 | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70E9 | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70EA | 1 | |
| Reserved | 0x00 70EB | 1 | |
| GPDDAT | 0x00 70EC | 1 | GPIO D Data Register |
| GPDSET | 0x00 70ED | 1 | GPIO D Set Register |
| GPDCLEAR | 0x00 70EE | 1 | GPIO D Clear Register |
| GPDTOGGLE | 0x00 70EF | 1 | GPIO D Toggle Register |
| GPEDAT | 0x00 70F0 | 1 | GPIO E Data Register |
| GPESET | 0x00 70F1 | 1 | GPIO E Set Register |
| GPECLEAR | 0x00 70F2 | 1 | GPIO E Clear Register |
| GPETOGGLE | 0x00 70F3 | 1 | GPIO E Toggle Register |
| GPFDAT | 0x00 70F4 | 1 | GPIO F Data Register |
| GPFSET | 0x00 70F5 | 1 | GPIO F Set Register |
| GPFCLEAR | 0x00 70F6 | 1 | GPIO F Clear Register |
| GPFTOGGLE | 0x00 70F7 | 1 | GPIO F Toggle Register |
| GPGDAT | 0x00 70F8 | 1 | GPIO G Data Register |
| GPGSET | 0x00 70F9 | 1 | GPIO G Set Register |
| GPGCLEAR | 0x00 70FA | 1 | GPIO G Clear Register |
| GPGTOGGLE | 0x00 70FB | 1 | GPIO G Toggle Register |
| Reserved | 0x00 70FC – 0x00 70FF | 4 |
Figure 6-12 shows how the various register bits select the various modes of operation for GPIO function.
NOTE
The input function of the GPIO pin and the input path to the peripheral are always enabled. It is the output function of the GPIO pin that is multiplexed with the output path of the primary (peripheral) function. Since the output buffer of a pin connects back to the input buffer, any GPIO signal present at the pin will be propagated to the peripheral module as well. Therefore, when a pin is configured for GPIO operation, the corresponding peripheral functionality (and interrupt-generating capability) must be disabled. Otherwise, interrupts may be inadvertently triggered. This is especially critical when the PDPINTA and PDPINTB pins are used as GPIO pins, since a value of zero for GPDDAT.0 or GPDDAT.5 (PDPINTx) will put PWM pins in a high-impedance state. The CxTRIP and TxCTRIP pins will also put the corresponding PWM pins in high impedance, if they are driven low (as GPIO pins) and bit EXTCONx.0 = 1.