JAJSFJ6C October 2012 – May 2018 TMS570LS0332 , TMS570LS0432
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1デバイスの概要
- 2改訂履歴
- 3Device Comparison
-
4Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 PZ QFP Package Pinout (100-Pin)
- 4.2
Terminal Functions
- 4.2.1 High-End Timer (N2HET)
- 4.2.2 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Modules (eQEP)
- 4.2.3 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 4.2.4 Controller Area Network Interface Modules (DCAN1, DCAN2)
- 4.2.5 Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface (MibSPI1)
- 4.2.6 Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI2)
- 4.2.7 Local Interconnect Network Controller (LIN)
- 4.2.8 Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converter (MibADC)
- 4.2.9 System Module
- 4.2.10 Error Signaling Module (ESM)
- 4.2.11 Main Oscillator
- 4.2.12 Test/Debug Interface
- 4.2.13 Flash
- 4.2.14 Core Supply
- 4.2.15 I/O Supply
- 4.2.16 Core and I/O Supply Ground Reference
- 4.3 Output Multiplexing and Control
- 4.4 Special Multiplexed Options
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for Clock Domains
- 5.6 Wait States Required
- 5.7 Power Consumption
- 5.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for PZ
- 5.9 Input/Output Electrical Characteristics
- 5.10 Output Buffer Drive Strengths
- 5.11 Input Timings
- 5.12 Output Timings
-
6System Information and Electrical Specifications
- 6.1 Voltage Monitor Characteristics
- 6.2 Power Sequencing and Power-On Reset
- 6.3 Warm Reset (nRST)
- 6.4 ARM Cortex-R4 CPU Information
- 6.5 Clocks
- 6.6 Clock Monitoring
- 6.7 Glitch Filters
- 6.8 Device Memory Map
- 6.9 Flash Memory
- 6.10 Flash Program and Erase Timings for Program Flash
- 6.11 Flash Program and Erase Timings for Data Flash
- 6.12 Tightly Coupled RAM Interface Module
- 6.13 Parity Protection for Accesses to peripheral RAMs
- 6.14 On-Chip SRAM Initialization and Testing
- 6.15 Vectored Interrupt Manager
- 6.16 Real-Time Interrupt Module
- 6.17 Error Signaling Module
- 6.18 Reset / Abort / Error Sources
- 6.19 Digital Windowed Watchdog
- 6.20 Debug Subsystem
-
7Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 7.1 Peripheral Legend
- 7.2 Multibuffered 12-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 7.3 General-Purpose Input/Output
- 7.4 Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET)
- 7.5 Controller Area Network (DCAN)
- 7.6 Local Interconnect Network Interface (LIN)
- 7.7 Multibuffered / Standard Serial Peripheral Interface
- 7.8 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder (eQEP)
- 8デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 9メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文に関する付録
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PZ|100
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PZ|100
発注情報
7.2.3 ADC Electrical and Timing Specifications
Table 7-4 MibADC Recommended Operating Conditions
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADREFHI | A-to-D high-voltage reference source | ADREFLO | VCCAD | V |
| ADREFLO | A-to-D low-voltage reference source | VSSAD | ADREFHI | V |
| VAI | Analog input voltage | ADREFLO | ADREFHI | V |
| IAIC | Analog input clamp current
(VAI < VSSAD – 0.3 or VAI > VCCAD + 0.3) |
–2 | 2 | mA |
Table 7-5 MibADC Electrical Characteristics Over Full Ranges of Recommended Operating Conditions(1)
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION/CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmux | Analog input mux on-resistance | See Figure 7-1 | 95 | 250 | Ω | ||
| Rsamp | ADC sample switch on-resistance | See Figure 7-1 | 60 | 250 | Ω | ||
| Cmux | Input mux capacitance | See Figure 7-1 | 7 | 16 | pF | ||
| Csamp | ADC sample capacitance | See Figure 7-1 | 8 | 13 | pF | ||
| IAIL | Analog off-state input leakage current | VCCAD = 3.6 V MAX | VSSAD < VIN < VSSAD + 100 mV | –300 | –1 | 200 | nA |
| VSSAD + 100 mV < VIN < VCCAD - 200 mV | –200 | –0.3 | 200 | ||||
| VCCAD - 200 mV < VIN < VCCAD | –200 | 1 | 500 | ||||
| IAOSB | Analog on-state input bias | VCCAD = 3.6 V MAX | VSSAD < VIN < VSSAD + 100 mV | –8 | 2 | µA | |
| VSSAD + 100 mV < VIN < VCCAD - 200 mV | –4 | 2 | |||||
| VCCAD - 200 mV < VIN < VCCAD | –4 | 12 | |||||
| IADREFHI | ADREFHI input current | ADREFHI = VCCAD, ADREFLO = VSSAD | 3 | mA | |||
| ICCAD | Static supply current | Normal operating mode | (2) | mA | |||
| ADC core in power-down mode | 5 | µA | |||||
(1) 1 LSB = (ADREFHI – ADREFLO)/ 2n where n = 10 in 10-bit mode and 12 in 12-bit mode
(2) See Section 5.7.
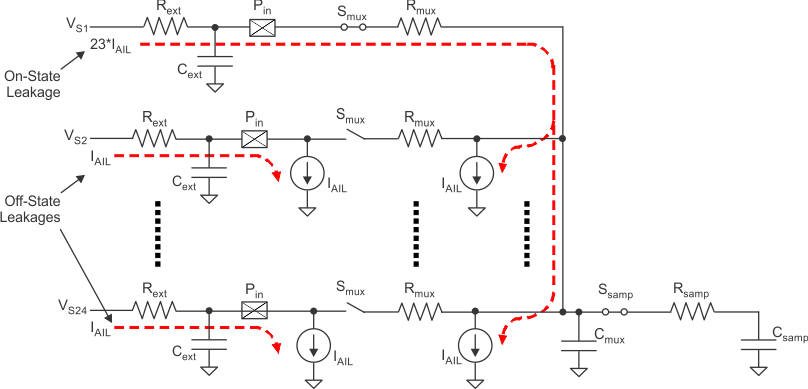 Figure 7-1 MibADC Input Equivalent Circuit
Figure 7-1 MibADC Input Equivalent Circuit Table 7-6 MibADC Timing Specifications
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tc(ADCLK)(2) | Cycle time, MibADC clock | 33 | ns | ||
| td(SH)(3) | Delay time, sample and hold time | 200 | ns | ||
| td(PU-ADV) | Delay time from ADC power on until first input can be sampled | 1 | µs | ||
| 12-BIT MODE | |||||
| td(C) | Delay time, conversion time | 400 | ns | ||
| td(SHC)(1) | Delay time, total sample/hold and conversion time | 600 | ns | ||
| 10-BIT MODE | |||||
| td(C) | Delay time, conversion time | 330 | ns | ||
| td(SHC)(1) | Delay time, total sample/hold and conversion time | 530 | ns | ||
(1) This is the minimum sample/hold and conversion time that can be achieved. These parameters are dependent on many factors for example, the prescale settings.
(2) The MibADC clock is the ADCLK, generated by dividing down the VCLK by a prescale factor defined by the ADCLOCKCR register bits 4:0.
(3) The sample and hold time for the ADC conversions is defined by the ADCLK frequency and the AD<GP>SAMP register for each conversion group. The sample time must be determined by accounting for the external impedance connected to the input channel as well as the internal impedance of the ADC.
Table 7-7 MibADC Operating Characteristics Over Full Ranges of Recommended Operating Conditions
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION/CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | Conversion range over which specified accuracy is maintained | ADREFHI - ADREFLO | 3 | 3.6 | V | |||
| ZSET | Offset Error | Difference between the first ideal transition (from code 000h to 001h) and the actual transition | 10-bit mode | With ADC Calibration | 1 | LSB(1) | ||
| Without ADC Calibration | 2 | |||||||
| 12-bit mode | With ADC Calibration | 2 | ||||||
| Without ADC Calibration | 4 | |||||||
| FSET | Gain Error | Difference between the last ideal transition (from code FFEh to FFFh) and the actual transition minus offset. | 10-bit mode | 2 | LSB | |||
| 12-bit mode | 3 | |||||||
| EDNL | Differential nonlinearity error | Difference between the actual step width and the ideal value.
(See Figure 7-2) |
10-bit mode | ± 1.5 | LSB | |||
| 12-bit mode | ± 2 | |||||||
| EINL | Integral nonlinearity error | Maximum deviation from the best straight line through the MibADC. MibADC transfer characteristics, excluding the quantization error.
(See Figure 7-3) |
10-bit mode | ± 2 | LSB | |||
| 12-bit mode | ± 2 | |||||||
| ETOT | Total unadjusted error | Maximum value of the difference between an analog value and the ideal midstep value. (See Figure 7-4) | 10-bit mode | With ADC Calibration | ± 2 | LSB | ||
| Without ADC Calibration | ± 4 | |||||||
| 12-bit mode | With ADC Calibration | ± 4 | ||||||
| Without ADC Calibration | ± 7 | |||||||
(1) 1 LSB = (ADREFHI – ADREFLO)/ 2n where n = 10 in 10-bit mode and 12 in 12-bit mode